In the grand theatre of architecture, the facade takes center stage, drawing the eye and setting expectations. Unlike any other design element, the facade blends form and function, weaving materials and aesthetics into a unique tapestry that encapsulates a structure’s personality. As the first sight-line into architectural ambition, it’s where innovation often meets reality.
Facades are the outward expression of a building’s soul, much like a book’s cover whispers of the story within. They achieve far more than mere ornamentation; they speak of history, culture, and geographical nuances while offering functional benefits like thermal efficiency and weather protection. Let’s delve into these canvases of urban art and uncover the layers of design and materials involved.
Key Features and First Impressions
- Aesthetic Appeal: The facade sets the tone, offering an initial visual impact that can range from the grandiose to the minimalist.
- Weather Resistance: It shields the interior spaces from the elements, playing a crucial role in building longevity.
- Thermal Efficiency: Modern facades contribute significantly to energy efficiency, helping lower overall costs.
- Material Versatility: Whether it’s glass, metal, or eco-bricks, the material choices are utterly diverse and evolving.
Each of these features serves a purpose beyond mere aesthetic enhancement, as the choice of materials and design can dictate a building’s resilience, energy conservation, and maintenance costs.
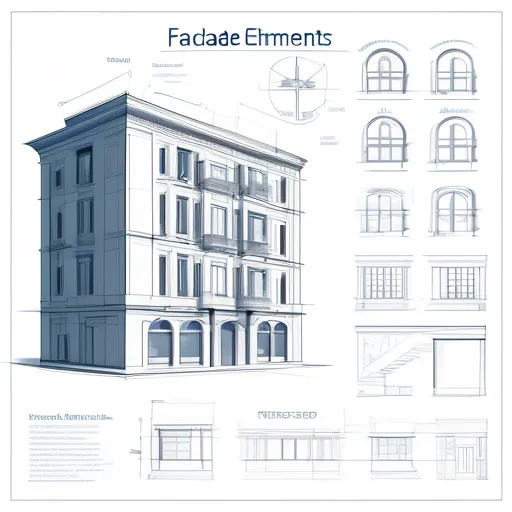
Technical Details
Design
Designing a facade combines artistry with engineering. Architects must balance creative ambition with structural feasibility. Be it the stark minimalism of modern cubist structures or the ornate detailing of Gothic replicas, each design must align with the building’s intended function and environmental context.
Performance
Performance is gauged by how well the facade withstands various environmental pressures, including wind, rain, and temperature fluctuations. The right facade can drastically improve thermal performance, thus reducing the overall energy footprint.
Usability
Usability in facade architecture translates to ease of maintenance and adaptability. For instance, innovations like double-skin facades offer improved thermal insulation while permitting natural ventilation, a feature that leads to more sustainable buildings.

Side-by-Side Comparison
| Aspect | Option A | Option B |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Glass Composite | Aluminum Panel |
| Ease of Use | Medium Maintenance | Low Maintenance |
| Design | Sleek Modern | Classic Robust |
| Operating Costs | Moderate | Low |
Choosing between glass composites and aluminum panels depends largely on the desired aesthetic and functional outcomes. If maintenance and lasting impact are priorities, low-cost solutions might emphasize more conservative panel options.
Practical Tips
- Consider local climate conditions when choosing facade materials to ensure durability and efficiency.
- Opt for materials that are not only sustainable but offer additional practical benefits, like reduced energy consumption.
- Innovate by repurposing materials — discover unique ways to use surplus materials for eco-friendly design choices.
- Balance aesthetics with functionality; the facade is an expression of both art and purpose.
Modern facades are not just about looking good; they represent an intersection of technology, efficiency, and style—paving the way for the future of construction.

As we stand on the cusp of architectural evolution, facades play an undeniable role in shaping our skylines and conserving resources. The choices made today will ripple into tomorrow, affecting everything from energy consumption to urban aesthetics.
Next time you consider a new project, think beyond simple walls and explore the possibilities inherent in every material and design approach. Perhaps you might even find inspiration for compact living solutions within the facade’s embrace. Ultimately, facades hold the potential to transform not just buildings, but the very air we breathe.
 “`html
“`html
FAQ
What are architectural facade components?
Architectural facade components are elements that make up the exterior appearance of a building. They play a crucial role in both the aesthetics and functional performance of structures.
Why are design concepts important?
Design concepts guide the visual impact and practical function of an architectural project. They ensure that facade components align with the desired aesthetic and purpose of a building.
What functional aspects do facades address?
Facades address aspects such as energy efficiency, weather protection, and natural light management. They contribute significantly to a building’s overall performance and sustainability.
What materials are used for facades?
Common materials for facades include glass, metal, stone, and composite panels. Each material offers unique properties that can enhance a building’s appearance and functionality.
“`