In the realm of construction, especially where safety finds itself in the heart of discussions, fire-resistant plasterboard (FRP) emerges as a modern-day paragon of protection and efficiency. This material, often overshadowed by its more mundane siblings in the drywall family, plays a critical role in minimizing fire hazards, thereby ensuring the security of structures and the lives within them.
Understanding the Essence of Fire-Resistant Plasterboard
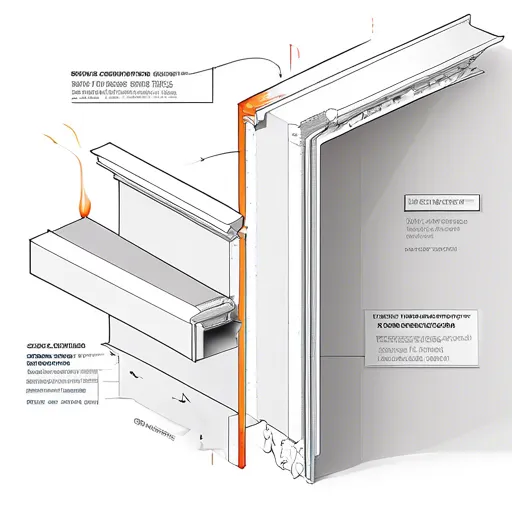
Fire-resistant plasterboard is a specially formulated type of drywall designed to withstand high temperatures and delay the spread of flames. Its core is fortified with non-combustible fibers and additives, which enhance its ability to endure fire exposure longer than regular drywall. This unique composition is not merely a technological gimmick; rather it is a crucial safety feature in the architecture of modern buildings.
Consider this: in a typical apartment fire, time is a luxury few can afford. Traditional plasterboard might succumb to heat quickly, but FRP acts as a bulwark, preventing the fire from leaping across walls and giving building occupants precious extra minutes to evacuate. This time can be the difference between tragedy and a safe escape.

When integrating such material into projects, architects and builders often find themselves balancing the scales of cost versus safety. But with the rising number of fire codes mandating the use of fire-resistant materials, opting for FRP is becoming less of a luxury and more of a necessity.
- Enhanced fire resistance due to specialized core additives.
- Compliance with stringent fire safety regulations.
- Increased structural life in the event of a fire.
- Peace of mind for occupants and property owners.
Where to Apply Fire-Resistant Plasterboard
The application of fire-resistant plasterboard is as varied as the buildings it protects. One can find its installation throughout residential, commercial, and even industrial settings. Specific zones within structures are particularly suited for FRP—think kitchens, furnace rooms, and even stairwells. These areas, prone to higher fire risks, benefit from the added layer of defense provided by fire-resistant materials.
In residential interiors, FRP is often utilized in bedrooms and living spaces, where its ability to restrict fire spread can save irreplaceable personal items and priceless family memories. Its use is not simply confined to safety, but extends into design aesthetics. Imagine a black and white bedroom where safety does not compromise style, perhaps drawing inspiration from Black and White Bedroom: Over 50 Photos and Creative Interior Design Ideas.
Commercial applications see fire-resistant plasterboard in offices and retail spaces where large numbers of people gather. Here, the priority is preventing devastation from both fire and the costly damages that accompany it. Moreover, complex structures like Interior design of a two-bedroom apartment. can integrate FRP seamlessly, enhancing safety without disrupting the design flow.
On an industrial scale, FRP finds its place in manufacturing facilities and storage buildings. These, often dealing with heavy machinery or combustible materials, rely on the plasterboard’s defensive capabilities to keep operations running literally and figuratively.
- Residential: kitchens, living spaces, bedrooms.
- Commercial: offices, retail stores, public spaces.
- Industrial: warehouses, factories, storage units.
- Public institutions: hospitals, schools, governmental buildings.
The Science Behind the Safety
At its core, fire-resistant plasterboard owes its functionality to a composition enriched with gypsum and glass fibers. When exposed to fire, the gypsum undergoes calcination—a process where it releases moisture in the form of steam, thereby slowing the fire’s advance. This moisture acts as a natural retardant, absorbing heat and reducing the temperature in adjacent rooms.
Studies suggest that the presence of this material can slow the spread of fire by up to 60 minutes, a critical interval for emergency services.
Beyond the materials themselves, how FRP interacts with other elements in a building is a crucial component of its effectiveness. The correct installation, with appropriate overlap and sealant use, fortifies walls against infiltration by heat and flame.
| Material | Fire Resistance | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Plasterboard | Up to 30 minutes | Ceilings, Non-critical Walls |
| Fire-Resistant Plasterboard | Over 60 minutes | Firewalls, Stairwells, Safety Exits |
| Glass Reinforced Gypsum | Varies (Enhanced) | Structural Panels, Exterior Assemblies |

Expert Tips for Optimum Use
Experts often share valuable insights into integrating FRP into existing homes or new constructions. They emphasize understanding that not all fire-resistant plasterboard is created equal. Matching the right type to its intended use is paramount. Opt for high-performance brands in areas of the home where safety is paramount—these offer the most robust protections.
“Investing in quality fire-rated materials does not just meet regulatory requirements; it builds lasting trust with homeowners and occupants alike,” notes an industry veteran.
It’s also important to consider complementary safety features. Pair FRP with smoke alarms, sprinkler systems, and accessible exit strategies for comprehensive fire safety protocols. The combination of these elements creates a holistic approach to fire safety, leveraging technology and intelligent design for maximum protection.
Moreover, home renovations present an opportunity to retrofit such safety measures. When updating a space—whether swapping out a wardrobe, for instance Sliding wardrobes: advantages, disadvantages and variety of designs—consider integrating fire-resistant walls as a part of the redesign. This approach ensures that modernization also equates with increased safety.
- Select quality FRP based on area-specific needs.
- Install alongside modern smoke and fire detection systems.
- Ensure correct installation for maximum efficiency.
- Regularly inspect and maintain FRP installations for ongoing safety.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
With the rising importance of FRP, certain pitfalls catch the unwary. A frequent mistake is insufficient adherence to detailed instructions during installation. FRP needs precise handling; improper installation can drastically reduce its fire retardant capabilities. It’s critical to follow protocols, ensuring seams are properly taped and gaps sealed to prevent fire passage.

Another oversight occurs in the material selection. Not all products are interchangeable. Commercial environments demand robust, commercial-grade options to meet regulatory standards, while residential settings might utilize lighter, eco-friendly alternatives. Industry experts continually stress the importance of selecting materials suited for specific applications, avoiding a one-size-fits-all mentality.
According to fire safety experts, “Compliance begins with the correct choice; installing what suits the environment paves the way to ensuring effective fire barriers.”
Lastly, the failure to account for future renovations can compromise FRP effectiveness. Before initiating changes or reconfigurations, assess how any structural alterations might affect installed fire barriers.
- Ensure meticulous adherence to installation data.
- Select appropriate material grades.
- Consider potential future changes during installation.
- Regular update of fire safety plans and material checks.
Future Trends in Fire-Resistant Materials
Innovation in fire-resistant technology continues its rapid pace. With a shift towards sustainability, manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly fire-resistant options. Materials infused with plant-based compounds are on the horizon, promising both safety and sustainability.
Furthermore, smart technology is making its way into fire safety. Imagine plasterboard that includes embedded sensors, alerting occupants and authorities at the first hint of trouble. This integration of technology with traditional materials is poised to redefine expectations in modern construction.
Moreover, evolving building standards are pushing for the use of top-tier fire-resistant materials. As our understanding of climate change and its impact on fire behavior evolves, so too will our approach to building safe, resilient spaces.
- Eco-friendly, sustainable materials are emerging.
- Smart technology integrations for advanced warning systems.
- Continual evolution of building codes requiring advanced fire safety solutions.
- Adaptation in design to build with resilience against changing climate patterns.
“`html
FAQ
What is fire-resistant drywall?
Fire-resistant drywall, also known as FRP, is a material designed to enhance fire safety in buildings. It provides an extra layer of protection against fire, ensuring the safety of occupants.
How does FRP enhance safety?
FRP enhances safety by delaying the spread of fire, giving occupants more time to evacuate. Its fire-resistant properties are critical in reducing damage and protecting lives.
What are the advantages of using FRP?
The advantages of using FRP include enhanced fire resistance and improved safety during emergencies. It also contributes to the structural integrity of buildings under high-temperature conditions.
Where is fire-resistant drywall optimally used?
Fire-resistant drywall is optimally used in areas that need increased fire protection, such as commercial buildings, hospitals, and multifamily residences. It’s particularly beneficial where fire codes require additional precautions.
“`