In the vast universe of construction materials, the age-old debate between solid and hollow bricks continues unabated. A casual observer might dismiss this as an esoteric topic, but delve deeper and you find nuanced considerations that can significantly affect your choice of bricks for your next building project.
Brief summary: This article unpacks the debate between solid and hollow bricks, addressing their characteristics, advantages, and ideal usage scenarios. It provides a comprehensive view on choosing the right type of brick for construction, including expert insights and practical observations.
Understanding the Basics of Solid Bricks
Solid bricks, the sturdy stalwarts of construction, boast a timeless reputation for durability. These dense blocks are usually free from holes, offering a robust structure to any building. Historically, these bricks have been used in monumental constructions—think ancient castles and temples where solidity was non-negotiable. Despite their weight, solid bricks are prized for their formidable strength, able to withstand the pressures of time and nature.
Contrary to what some might expect, solid bricks can offer thermal mass benefits, absorbing heat during the day and releasing it at night. This natural regulation contributes to more stable temperatures within a building. However, the heavy nature of these bricks makes them less ideal for regions where earthquake resistance is paramount, as their weight increases the building’s seismic load. When considering rustic aesthetics, nothing matches the heritage feel conferred by solid bricks, a choice aesthetic purists adore.
Yet, these positives don’t overshadow some practical challenges. For instance, solid bricks are harder to transport and lay due to their weight, potentially inflating project costs. In conclusion, while solid bricks are a builder’s treasure for certain projects, they come with their set of logistical complexities. Therefore, the choice to use them demands careful consideration of the project scope and budget constraints.
Hollow Bricks: A Modern Marvel
On the flip side, hollow bricks have gained traction as a modern building material for their unique advantages. Distinguished by their lighter nature due to the cavities within, these bricks offer superior insulation properties. The numerous air pockets inside help reduce heat transfer, leading to a more energy-efficient home. Modern construction often favors hollow bricks for these benefits, particularly in regions with fluctuating temperatures.
Hollow bricks come equipped with another sneaky advantage: easier utility installation. Running pipes and wires through these cavities can save time and reduce labor costs—a dream for quick modern builds! Furthermore, they exert less load on the foundation, which can be a lifesaver in seismic zones where structural flexibility is crucial. Hollow bricks promise speed in construction, a significant plus in today’s fast-paced building climate.
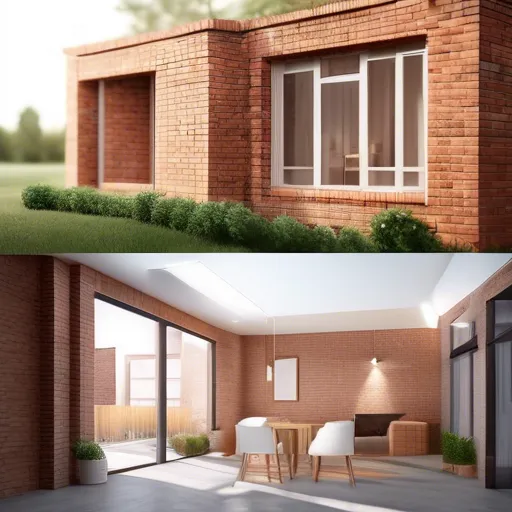

Despite these merits, hollow bricks face their set of criticisms. Questions about their durability linger, especially under highly stressful conditions like heavy storms or impact scenarios. Yet, in an era that values energy-efficiency and eco-friendliness, these bricks tick many boxes. Therefore, their application is often seen as a forward-thinking choice aligned with modern sustainability goals.
Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Efficiency in building is more than just a buzzword—it’s a tangible measure of how materials interact with the environment. Solid bricks, with their high-density construction, can be more cumbersome in terms of the carbon footprint of production and transport. Meanwhile, hollow bricks shine in this department, often made with materials and processes that emphasize sustainability.
Moreover, the reduced weight of hollow bricks minimizes logistical impact. Distributors relish in their ability to move more units at lesser cost and environmental toll. This difference not only impacts the immediate costs but offers long-term savings in terms of reduced energy needs for climate control within buildings.
A Apartment design 44 m²: layouts, decor features and stylish ideas (47 photos) often exemplifies how lightweight materials can enhance design flexibility, thereby complementing aesthetic aspirations.
According to a recent study, buildings constructed with hollow bricks demonstrated a 20% increase in energy efficiency, showcasing their relevance in today’s eco-conscious construction landscape.
In conclusion, choosing hollow bricks can represent a step toward greener building practices, aiding not just in reducing upfront emissions, but also in fostering long-term ecological responsibility.
Durability and Lifespan: What You Should Know
In construction, longevity and resilience are paramount. Solid bricks, as veterans of the trade, often headline durability discussions. Their resilience against natural erosions, moisture, and the elements is well documented. These bricks endure, steadfast, through generations—a key draw for projects requiring long-term structural integrity.
Hollow bricks, however, challenge this perception by presenting viable durability through modern engineering. Technological advancements have bolstered their strength, allowing them to compete with traditional options under various conditions.

Regional climates significantly influence the effectiveness of these materials. While solid bricks excel in stable climates, hollow bricks can suffer cracks through thermal cycling in extreme weather zones, a factor worth noting for interested builders.
Expert note: “For projects in areas prone to seismic activity, choosing hollow bricks can mitigate risk due to their inherent flexibility and lower weight. This can greatly enhance both structural safety and occupant peace of mind.”
Thus, while solid bricks maintain tradition’s reliability, hollow bricks continue to evolve, adapting to new challenges with innovative solutions. Both types present compelling cases when analyzed through the lens of durability.
How to Choose Between Solid and Hollow Bricks
Deciding on the type of brick for your construction project can be a daunting task. It’s essential to weigh the purpose of the building in conjunction with environmental factors. A house designed for a region with frequent temperature fluctuations might benefit from hollow bricks due to their insulation properties.
By contrast, a heritage site restoration may demand the authenticity of solid bricks to match historical accuracy. In urban planning, where budget and timeline are often key constraints, hollow bricks can offer an edge in efficiency without compromising structural integrity.

Step-by-Step Decision Making
1. Assess the environmental conditions: Evaluate the climate and typical weather patterns.
2. Determine the building’s function: Align material choice with the purpose—residential, historical, commercial.
3. Consider economic factors: Analyze cost implications both in the short and long term.
4. Factor in aesthetic goals: Decide how the brick aligns with the broader design vision.
In the end, aligning project needs with brick features is crucial. As explored in various design examples, like the 68 Modern Wallpaper Ideas for Girls’ Rooms: Photo Gallery in Interior, different bricks can complement distinct aesthetics and functions.
Statistics from the building industry reveal that 68% of contractors favor hollow bricks for urban development owing to their cost-effectiveness and eco-friendly properties.
Therefore, the right choice stems from a harmonious blend of practical needs, economic constraints, and personal creativity.
Comparative Analysis: Solid vs. Hollow Bricks
| Characteristic | Solid Bricks | Hollow Bricks |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Insulation | Moderate | High |
| Durability | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
A deeper evaluation shows that while both brick types excel in specific scenarios, choosing between solid and hollow bricks comes down to matching the material with the project requirements.
Conclusion: Balancing Pros and Cons
Weighing the quirks and features of both solid and hollow bricks reveals more than a simple dichotomy—it’s a nuanced decision grounded in context and project goals. It’s not merely about the solidity or hollowness but understanding the implications of your choice. The essence lies in aligning these characteristics with site needs, aesthetic desires, and practical realities.
Explorations in home care, such as How to effectively wash the floor: by hand or with a mop? – 8 arguments for and against., replicate similar deliberations—balancing tradition with innovation.
In conclusion, whether dipping toes into modern architecture or restoring historical grandeur, the choice between solid and hollow bricks reflects more than materials—it’s a narrative of vision, constraints, and aspirations within the colorful tapestry of construction.
- Solid bricks excel in durability and thermal mass.
- Hollow bricks offer enhanced insulation and reduced weight.
- Project scope and climate influence the choice.
- Both types hold unique advantages and limitations.
- Expert insights emphasize modern sustainability goals for hollow bricks.
“`html
FAQ
What are the main differences between solid and hollow bricks?
In construction, solid bricks are denser and heavier, providing robustness and excellent load-bearing capacity, ideal for foundations and load-bearing walls. In contrast, hollow bricks include voids or cores that make them lighter, reducing structural weight and improving thermal insulation. Many builders choose depending on their specific project needs. For instance, hollow bricks are favored for non-load-bearing walls in modern apartments for their insulation benefits, while solid bricks are preferred for their strength in older homes. In practice, the choice impacts construction techniques and energy efficiency, a crucial consideration during planning.
Which type of brick is more cost-effective for construction?
The cost-effectiveness of solid versus hollow bricks can vary based on regional availability and specific project demands. However, hollow bricks typically offer long-term savings due to their superior insulation, potentially reducing heating and cooling costs in homes or offices. Although initially costlier than solid bricks, their lightweight nature reduces transportation and handling expenses. In contrast, solid bricks could be more economical upfront, especially for projects demanding fewer materials and labor. Builders should evaluate initial costs against future energy savings. In real-world applications, overlooking these factors might lead to unforeseen expenses.
What are the advantages of using solid bricks in construction?
Solid bricks are renowned for their strength and durability, making them a staple in constructing buildings that require robust support and stability, such as tall structures or retaining walls. These bricks provide excellent sound insulation, which is invaluable in busy city centers where noise reduction is a priority. In old residential projects, the use of solid bricks has shown long-lasting performance against natural elements, contributing to their charm. Notably, architects often incorporate solid bricks in designs that stress durability, showcasing both aesthetic appeal and practical robustness. Property owners frequently appreciate the enduring character these bricks promote.
What benefits do hollow bricks offer that solid bricks do not?
Hollow bricks excel in areas where thermal efficiency and weight reduction are critical. Due to their air voids, they provide superior thermal insulation, helping maintain a comfortable indoor climate by minimizing heat transfer. This also contributes to energy savings in both heating and cooling climates. Their lightweight nature makes them easier to handle and reduces the structural load, beneficial in earthquake-prone regions or high-rise buildings. A prime example can be observed in modern suburban homes where builders use hollow bricks to achieve eco-friendly goals without sacrificing aesthetic design. However, careful planning is essential to avoid structural stability issues.
Are there any limitations to using solid bricks in modern construction?
Solid bricks, while robust, also come with notable limitations. Their heaviness can increase construction time and costs, demanding more labor and stronger foundation support. In sustainable or energy-efficient builds, their lower thermal insulation capabilities may not align with modern energy standards unless complemented with additional insulation strategies. Moreover, due to their density, they might not be the ideal choice for earthquake-prone zones, where flexibility is crucial. Builders should consider these factors early in the design process to prevent escalated costs and ensure compliance with local building codes. These potential pitfalls highlight the importance of strategic planning in project efficiency.
What are common mistakes made when choosing between solid and hollow bricks?
A typical error is neglecting local climate and environment when selecting brick types. Choosing solid bricks for regions with extreme temperature variability can lead to higher energy costs due to inadequate insulation. Conversely, using hollow bricks for critical load-bearing structures without adequate reinforcement can compromise stability. Moreover, some developers underestimate the long-term benefits of insulation and lightweight applications. It’s essential to tailor brick choice to specific building requirements, considering structural, climatic, and economic aspects, to avoid unnecessary complications and ensure the longevity and safety of the construction.
How do I determine the right type of brick for my construction project?
Selecting the ideal brick type requires assessing several factors: structural needs, environmental conditions, and energy efficiency goals. For high-load areas, solid bricks are better suited due to their strength, whereas hollow bricks are beneficial in regions aiming for improved thermal insulation and reduced building loads. Consulting with construction professionals and reviewing local building codes is wise. A micro-example could be in new commercial buildings where architect feedback might steer choices towards materials that enhance both functional and aesthetic design goals. Engaging experts ensures a balanced decision tailored to the project’s unique demands, ultimately achieving a cost-effective and enduring outcome.
What are the approximate costs involved with solid and hollow bricks?
Typically, solid bricks are less expensive per unit due to simpler manufacturing processes and material requirements. Despite higher upfront costs, hollow bricks often yield financial benefits over time owing to reduced energy bills and structural load. Builders also report lower transportation costs thanks to their lighter weight. A comprehensive cost analysis should factor in not just the initial purchase price but also potential long-term savings in utilities and maintenance. Real planning saves property developers from unexpected expenses related to thermal inefficiencies or excess material handling, emphasizing strategic financial forecasting in construction budgeting.
“`
