Recommendations for choosing sizes
The standard dimensions of greenhouse structures on the site are 3 meters in length, 4-8 meters in width. This area is enough to successfully grow vegetable crops for one family.
The size of the beds for greenhouses depends on what exactly you are going to grow in them:
- Cucumbers. Since the leaves are voluminous, the width of the beds in the greenhouse should be maximum: 100-120 centimeters – in other conditions, the plants will not have enough sunlight.
- Tomatoes. To grow tomatoes in one row, 60 cm is enough, if the variety is tall, you can increase the depth of the bed to 80.
- Pepper. Bell peppers also require 60-70 centimeters of free soil.
- Lettuce. Useful greens, unlike vegetables, are undemanding to the place of cultivation. They will grow in narrow and wide, deep and shallow boxes.
Not only the length or width is important, but also the height. The higher the box, the warmer the plants will be in the off-season (the earlier they can be planted), but in the summer they will need to soak the soil with water more often and more often. The lower, the less often watering is needed, but such a greenhouse will only be good in the summer. The average generally accepted height of beds in a greenhouse is 10-30 centimeters.
We will discuss the location of the beds in the greenhouse and their number in one of the following sections, but first let’s find out what they are made of.

What are the beds made of?
You can make beds in a greenhouse from any available or special materials:
- boards;
- slate;
- brick;
- wood-polymer composite;
- lawn border;
- galvanized sheets;
- gabions;
- concrete.
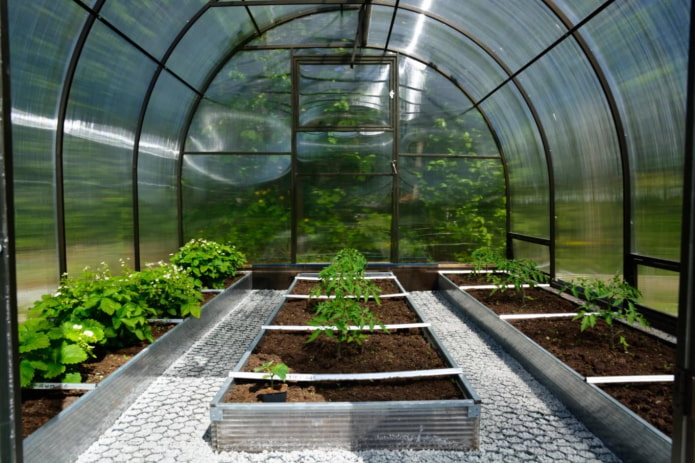

To choose the right material, pay attention to the properties. A suitable fence for beds in a greenhouse should be strong, not afraid of water and not change the composition of the soil.
Important! Although wood is afraid of water, it still remains one of the favorite materials among gardeners. Natural, cheap and easy to process. And to prevent the walls from rotting from watering and spraying, the wood is treated with protective impregnations, and covered with film from the inside.
How can the beds be arranged?
For dimensions of 3 * 6 (3 * 4, 3 * 8 m), 3 schemes of beds in a greenhouse are suitable:
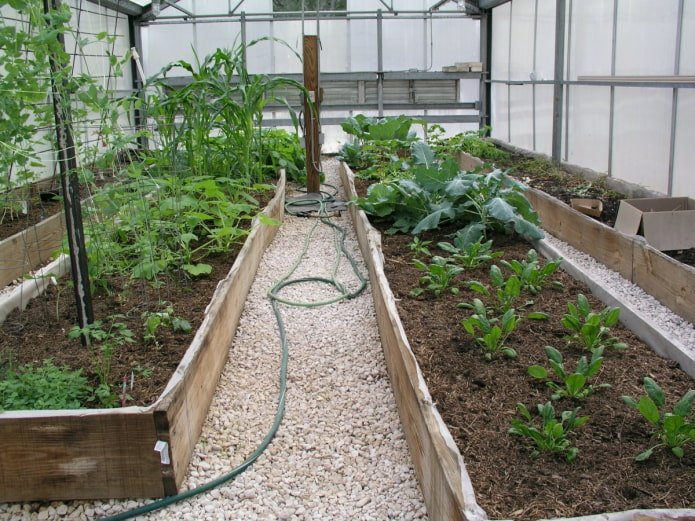
- Parallel. The arrangement of two rectangular beds (100-120 cm) along the long sides at the edges, a wide passage (60-100 cm) between the rows.
- Triple. There are 3 beds inside: a wide one (100-120 cm) in the center, 2 narrow ones (40-50 cm) along the walls. 80-120 centimeters will remain for paths between the rows. Another option is three rows of the same width (60-70 cm).
- U-shaped. The same dimensions as the previous one, but two parallel outer ridges are connected by a jumper in the far part of the greenhouse (see photo). Space for paths 0.8-1.2 m wide is also left in the shape of the letter U.
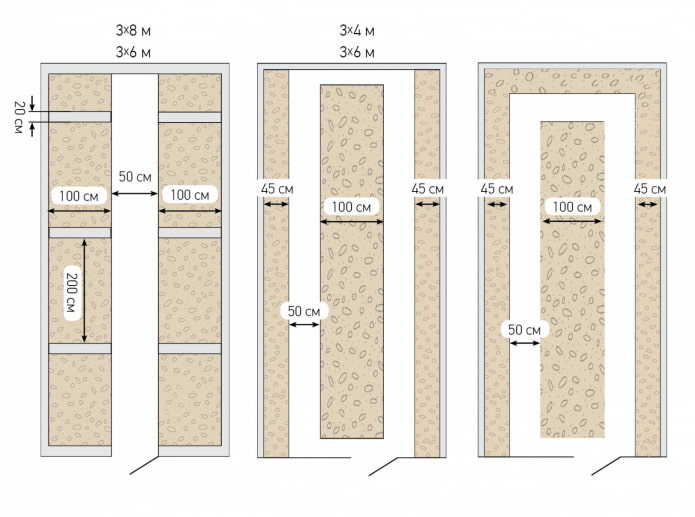
Important! The width of a bed in a greenhouse should not exceed 1.2 m (central), 1 m (side) – this is the optimal size, allowing you to care for plants from the passage.
Keep in mind: the greater the depth from the entrance to the far wall (the longer the greenhouse), the simpler the planning should be used. In 6-8 meter narrow greenhouses, place the beds on two sides, leaving the central part free for better air circulation.
Tip! If you use a garden wheelbarrow, measure its width first. The distance between the beds should be sufficient for passage.
When installing a greenhouse, try to place it in the direction from west to east: in this case, the crops grown will receive enough light. Is the greenhouse already mounted from north to south? The beds in the greenhouse should be arranged so that the tall plantings are in the north.
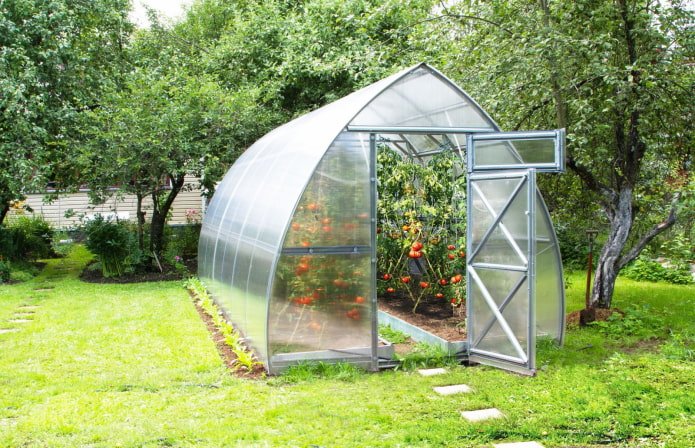

How to do it yourself?
For those who have theoretical knowledge, the arrangement of beds in the greenhouse will not be difficult. The instructions differ only slightly depending on the material you plan to use.
Wood
You will need:
- the boards themselves;
- timber as support posts;
- saw or jigsaw for cutting;
- tape measure;
- pencil;
- fasteners (nails, screws);
- screwdriver or screwdriver;
- mallet.
Step-by-step instructions:
- Preparation. First, measure the required dimensions of the boards (2 along the length of the greenhouse, 2 along the width), bars (board height + 25 cm), saw off. The surface needs to be sanded (to prevent splinters from getting into your hand or foot), and treated with a protective compound (against moisture and insects). The preparatory stage takes up most of the time.
- Assembly. Knock together a box from the boards, install the leg bars in the inner corners. You can additionally secure 1-2 bars on the long side for a secure base.
- Installation. Place the box with the protruding bars toward the ground, press down, tap with a mallet, sinking the legs into the ground. If the soil is dense, it is more convenient to install the bed with a shovel.
It remains to add a layer of humus, fill the soil and you can plant the seedlings.

Slate
The set of tools and materials is slightly different:
- sheets of flat slate of the required height;
- profile pipe;
- drill;
- drill with a carbide tip or for metal;
- roofing screws;
- grinder or circular saw.
All you need to do is:
- saw the slate strips to the required size,
- drill holes for the screws,
- screw the sheets to the profile, leaving 2-3 mm of free pipe edge on top to drive the structure into the ground.

Important! If the box is long enough, it is recommended to reinforce it with metal crossbars in 1-3 places.
See the video for an example of a bed made of flat slate:
In addition to regular beds, there are also special warm ones: they are easy to maintain, have fast plant growth, and produce a good harvest. The height of a warm bed is 50-70 centimeters, which is convenient in an open area, but not practical in a greenhouse.
Since greenhouse structures have slightly inclined or beveled edges, a high box cannot be installed close to the wall. And growing seedlings will be uncomfortable in cramped conditions.
Therefore, a trench option is chosen for greenhouses: a trench is dug approximately half (25-35 cm) of the total height, due to which the above-ground section turns out to be a standard 30-centimeter one. The top box can be assembled from scrap materials.
The difference between a warm bed and a regular one is not the fence, but the internal filling.
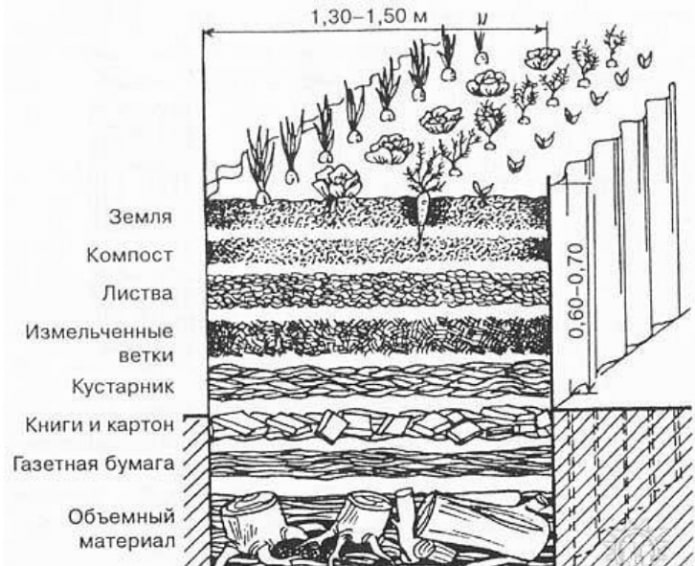
The warm bed is assembled layer by layer:
- Protection. The metal mesh at the bottom will prevent small rodents from feasting on greenhouse vegetables.
- Drainage. Large and small branches are a natural drainage material that does not allow water to stagnate and roots to rot. In addition, the branches retain and generate heat. It occupies about half of the total height.
- Organic matter. It occupies most of the remaining land and is a storehouse of nutrients for future plants. First, newspapers or cardboard are laid on top of the drainage – they will not allow the small fraction of compost to crumble down, and will preserve the “airiness” of the filler. Then we move layer by layer from large to small: branches, leaves, humus. The finished compost between the soil and undecomposed organic matter not only gives nutrients to the green inhabitants above, but also starts the decomposition processes from below.
- Soil. The very last layer is quite thin – about 20% of the total height – that is, 10 centimeters from a half-meter ridge. You can pour in soil dug from a trench, or buy soil separately: purchased mixtures have a different nutrient composition, are suitable for growing garden crops in greenhouses.
When arranging the beds, do not forget about fertilizers.
- Radiance. Microbiological fertilizer from BakSib, which starts rotting processes.
- Ash. Alkalizes overly acidic soils.
- Manure. Natural “heater” of the soil.
- Chalk. Strengthens roots, protects against bactericidal infection.
Efficient cultivation of crops in a greenhouse is not luck, but competent organization. Using the information from this article, you can be sure that any plants will not only grow well, but also bear fruit abundantly.
Now reading:
- Bed at a height: more than 40 photos of interiors and modern design solutions.
- How to decorate a bathroom on a budget? 7 best affordable solutions.
- Your Ultimate Guide to BMW Pre-Owned Vehicles
- Blue Living Room: 45 Interior Design Ideas and Color Combinations.
- Black sofa in design: more than 50 photos and ideas for the living room, kitchen and children’s room